1.多线程的实现
多线程有两种实现方式:
1.1.继承Thread类 =>示例:A a=new A(); a.start();

1.2.实现Runnable接口 =>示例:A a=new A(); new Thread(A,自定义线程名称).start();

其实Thread和Runnable都实现了run方法,这种操作模式其实就是代理模式
获取当前线程名称:Thread.currentThread().getName()
调用线程是thread.start(),真正执行线程是 thread.run()
具体代码:
1 /** 2 * 继承Thread类 3 * @date 2019/3/29 11:19 4 */ 5 public class SimpleThread extends Thread{ 6 7 @Override 8 public void run() { 9 super.run();10 Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();11 System.out.println("Thread =>当前执行的线程为:"+thread.getName());12 }13 }14 15 /**16 * 实现Runnable接口17 * @date 2019/3/29 11:2818 */19 public class SimpleRunnable implements Runnable {20 21 @Override22 public void run() {23 Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();24 System.out.println("Runnable =>当前执行的线程为:"+thread.getName());25 }26 }27 28 public class TestMain {29 30 31 /**执行线程示例1*/32 private static void callSimpleThread(){33 int index=10;34 for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {35 Thread thread=new SimpleThread();36 thread.start();37 }38 }39 40 /**执行线程示例1*/41 private static void callSimpleRunnable(){42 int index=10;43 for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {44 SimpleRunnable simpleRunnable=new SimpleRunnable();45 new Thread(simpleRunnable,"Runnable-"+i).start();46 }47 }48 49 public static void main(String[] args) {50 51 callSimpleThread();52 53 callSimpleRunnable();54 }55 56 }
2.多线程安全问题
2.1线程不安全示例
多线程最容易产生的一个问题就是线程安全问题,下面使用一个卖票的例子来体现。
场景描述:现在有两个售票员,一共卖10张车票
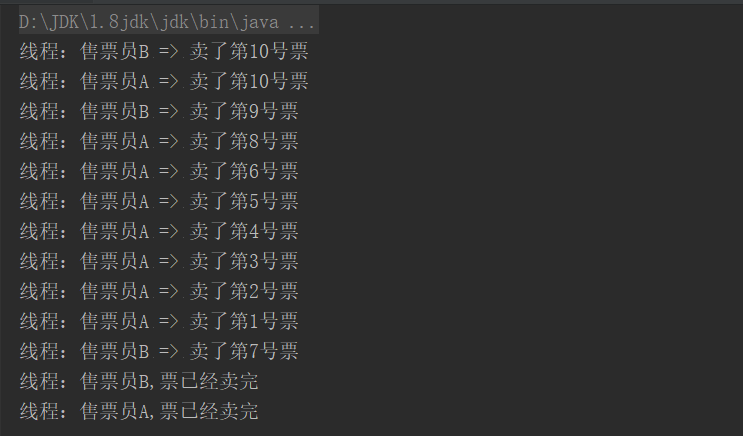
1 public class SellTicket extends Thread { 2 3 private static int NUMBER = 10; 4 public SellTicket(String name) { 5 super(name); 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public void run() {10 String s = "线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName();11 12 while (NUMBER > 0) {13 int i = NUMBER--;14 System.out.println(s + " => 卖了第" + i + "号票");15 }16 17 System.out.println(s + ",票已经卖完");18 super.run();19 }20 21 22 public static void main(String[] args) {23 24 SellTicket thread1 = new SellTicket("售票员A");25 thread1.start();26 27 SellTicket thread2 = new SellTicket("售票员B");28 thread2.start();29 30 }31 32 } 执行结果如下:
我们发现售票员A 和售票员B都卖了10号票,这就是线程不安全导致的结果
2.2线程不安全解决方法
方案一:使用同步代码解决 格式:synchronized(锁对象){需要被同步的代码} 锁对象可以为this锁,也可以自定义对象锁 方案二:使用同步函数解决 同步函数就是使用synchronized修饰一个函数
下面采用同步代码块解决
1 public class SafetySellTicket extends Thread { 2 3 private static int NUMBER = 10; 4 5 @Override 6 public void run() { 7 String s = "线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName(); 8 9 while (NUMBER > 0) {10 synchronized (this) {11 if (NUMBER > 0) {12 int i = NUMBER--;13 System.out.println(s + " => 卖了第" + i + "号票");14 } else {15 System.out.println(s + ",票已经卖完");16 break;17 }18 19 }20 }21 super.run();22 }23 24 25 public static void main(String[] args) {26 27 SafetySellTicket thread1 = new SafetySellTicket();28 thread1.start();29 30 SafetySellTicket thread2 = new SafetySellTicket();31 thread2.start();32 33 }34 35 }